Bits & Watts: Optimizing Energy and Cost in Renewable Grid System: an electrochemical modeling approach
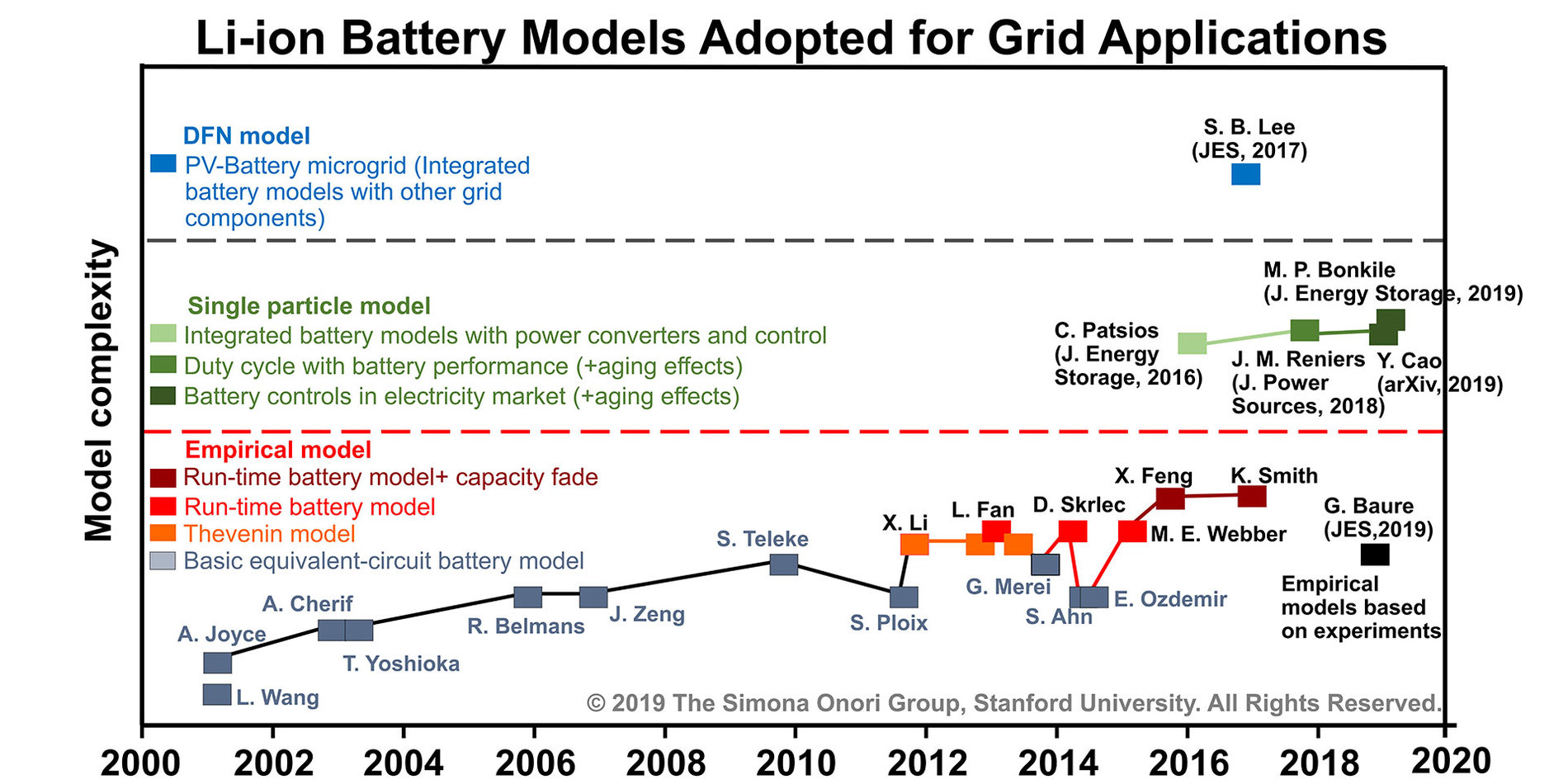
Today, lithium-ion batteries are considered the best means to store the energy to keep the balance between electricity generation and demand. Among different renewable energy applications, significant energy and cost savings can be achieved by optimal battery participation strategies enabling greater depth of discharge, smaller size, and longer life for renewable grid systems, typically ranging in size from kilowatts (microgrid) to megawatts (power grid).
Conventional approaches to model the renewable grid-storage systems adopt empirical/electrical equivalent circuit-based models that suffer from high calibration effort, lack of knowledge of electrochemical states, inadequateness of capturing degradation mechanisms and therefore predicting aging trajectories.
Our lab focuses on developing physics-based battery models and implementing them into the renewable grid systems, to help minimize the overall costs of the entire microgrid or power grid system. Advances on electrochemical battery modeling hold the potential to optimize battery system design and enhance its utilization for cost and resource reduction. This will set a new framework to evaluate future integrated renewable energy and storage systems models, which at the same time, can evolve to capture and explore emerging trends in grid storage technologies and systems.
This research is sponsored by Bits & Watts read more about our project here
